Hello Everyone
My Name is Minhaj Ahmad Khan and I'm a Front-End developer. This is my first blog where I create a REST API using NodeJS, ExpressJs, MongoDB, and Mongoose. I'm super excited so let's get started.
A REST API (also known as RESTful API) is an application programming interface that conforms to the constraints of REST architecture. REST stands for representational state transfer. Application programming interfaces (APIs) are everywhere. It is a software that allows two applications to communicate with each other over the internet and through various devices. Every time you access an app like Instagram or check the weather on your smartphone, an API is used.
Prerequisite
Node
MongoDB
Create a repository
Express
Mongoose
Nodemon
Postman
Install Node
If you have already Node on your machine then skip this step. Know How To Download & Install Node.js
Install MongoDB
if you have already MongoDB on your machine then skip this step. Know How To Download & Install MongoDB
Install Express
Express is a fast, assertive, essential, and moderate web framework of Node.js that helps manage a server and routes.
Let's install Express by running this command on the shell.
npm install express
Install Mongoose
Mongoose is a way to make a connection with the MongoDB database. It provides MongoDB validation and query in a very simple manner and it makes development fast.
Let's install Mongoose with Node by running this command on shell
npm install mongoose
Install Nodemon
Nodemon is a tool that helps develop Node. js based applications by automatically restarting the Node application when file changes in the directory are detected.
Let's install Nodemon by running this command on shell
npm install Nodemon
Postman
Postman is a great tool when trying to dissect RESTful APIs made by others or test ones you have made yourself. Know How To Download & Install Postman
We now have everything needed to start building our API.
Let's Code
We are going to create a RESTFUL API that maintains student records. We will perform Create, Read, Update, Delete (CRUD) Operation. These are the following steps
Create Repository
At Boilerplate
Connect to MongoDB
Define Schema
Write CRUD Operation
1. Create a repository
Let's create a repository called RestfulAPI
Open RestfulAPI repository on shell
npm init -y initializing our project
Now we can see the package.json file which will include all the packages we need.
2. Add Boilerplate
Let's write some javascript that will initialize and define endpoints in app.js avoid get() we discuss after a while.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000 ;
app.get('/', (req,res)=>{
res.send('<h1>this is home page of Student Api </h1>')
})
app.listen(port , ()=>{
console.log(`connection is extablished`)
});
Require express now we got express as a function and create new constant with the help of express for use express method and properties.
listen() method creates a listener on the specified port or path.
Let's run this code nodemon src/app.js and see what happens
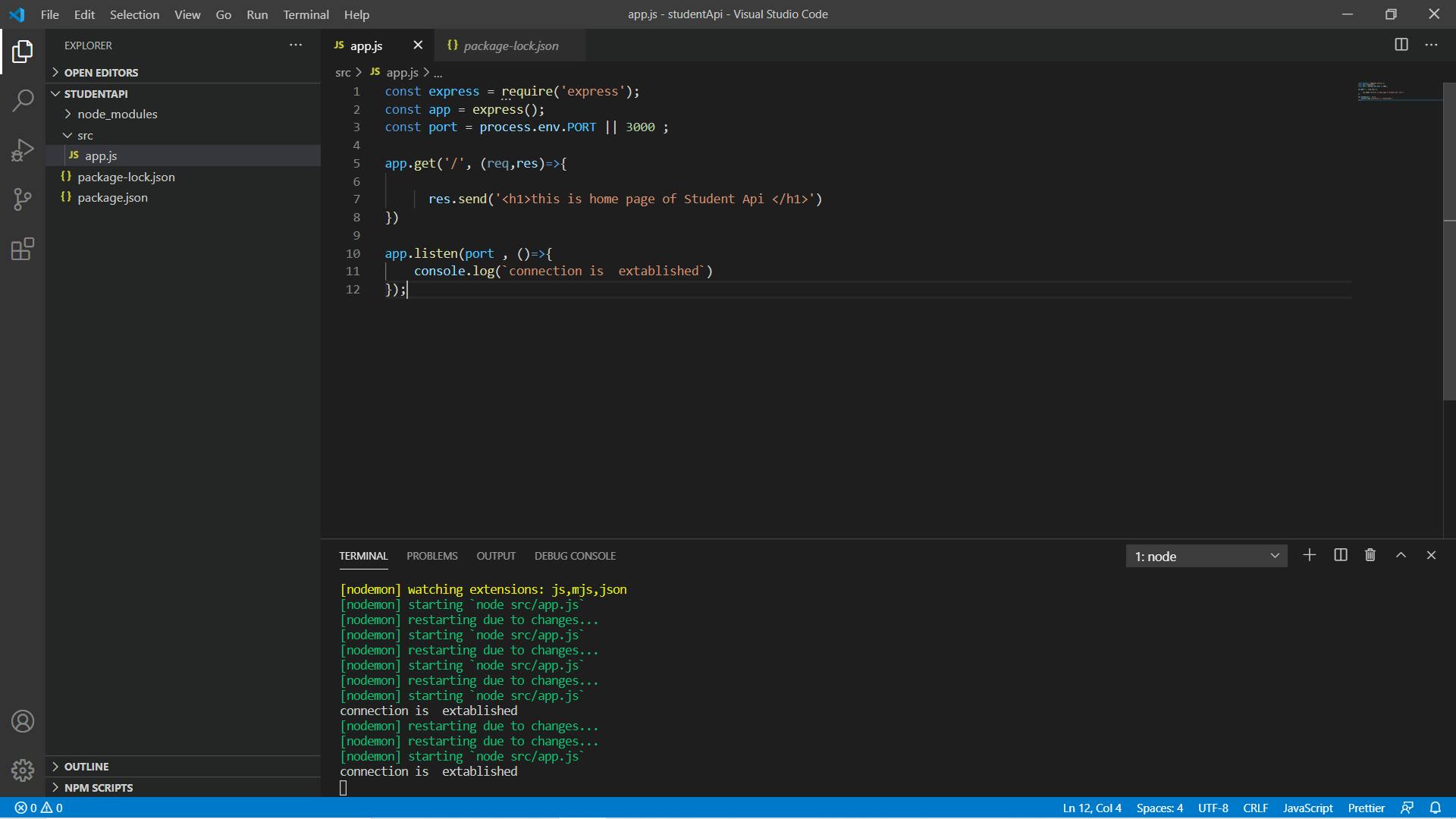
Cool! the connection is established let's move forward
3. Connect to MongoDB
Let's connect MongoDB with mongoose
for that, we need to create a folder and file inside src folder src/database/connection.js where write some javascript code to connect to MongoDB to the mongoose.
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
let url = process.env.DATABASE_URL || "mongodb://localhost:27017/students-record";
mongoose.connect(url, {
useCreateIndex: true,
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
}).then(() => {
console.log('connection successful')
}).catch((e) => {
console.log(`connection unsuccessful ${e}`)
})
As we can see in the above code block we are using mongoose.connect() method to connect to MongoDB database.
We need this to connect the student record database running locally on the default port (27017).
Then we need to call the connect function with the help of mongoose where we pass URL and a call back function that returns a promise. To avoid
deprecation Warnings set useCreateIndex: true,
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
We need to require connection.js in our express file (app.js) require('./database/connection')
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000 ;
require('./database/connection')
app.post('/studentregistration', (req,res)=>{
res.send('<h1>this is home page of Student Api </h1>')
})
app.listen(port , ()=>{
console.log(`connection is extablished`)
});
Now run app.js file and see what happens
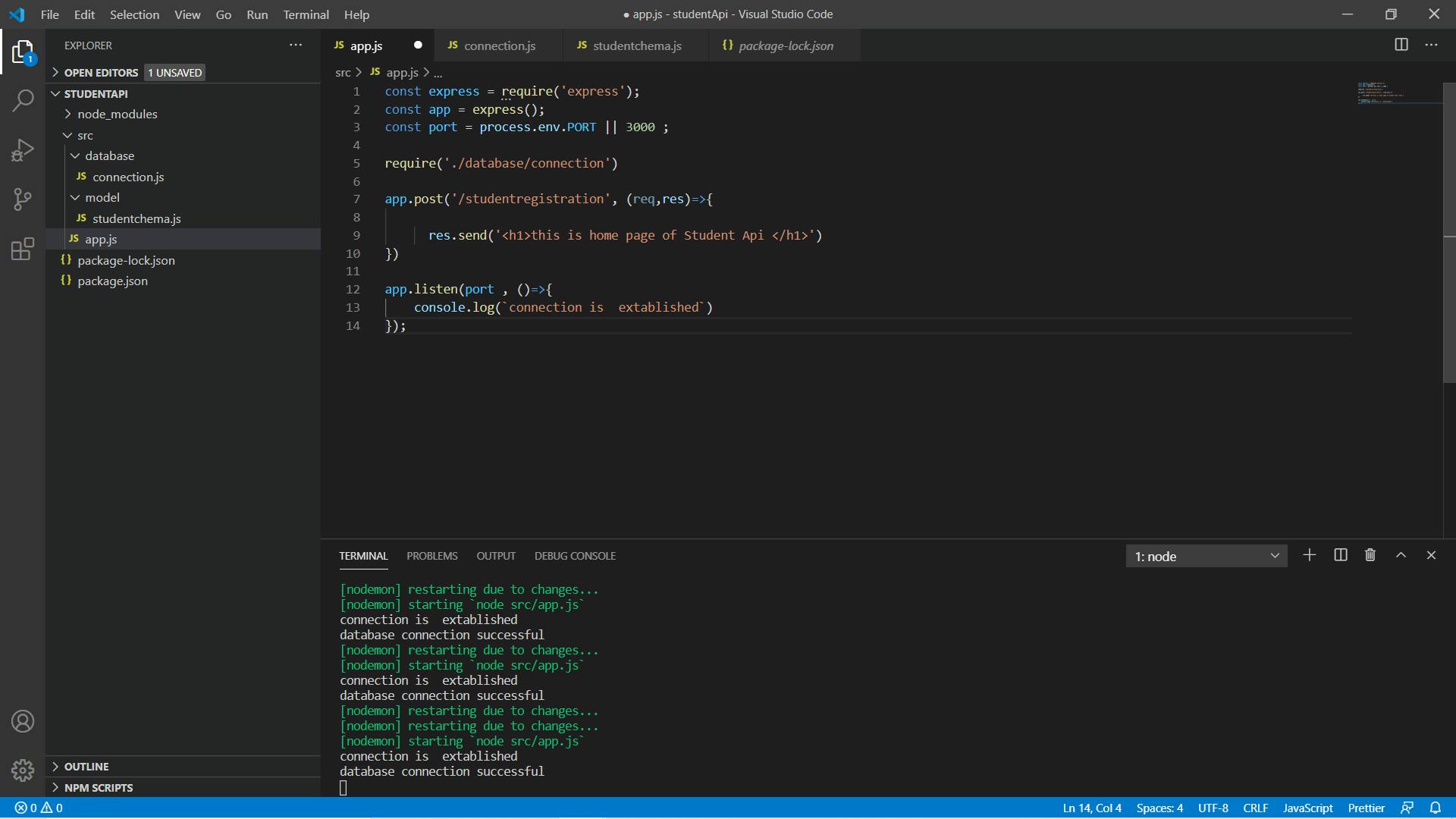
Cool! database connection was successful
4. Defining Schema
Now let's define our database schema for that we need to create a folder and file inside src src/model/student-schema.js. To know more about schema read official document here
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const student-schema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String,
required: true,
minlength: 3,
},
class : {
type:String,
},
email: {
type: String,
required: true,
unique: true,
},
phone: {
type: Number,
required: true,
maxlength: 10,
minlength: 10
},
address: {
type: String,
required: true,
}
})
const student = new mongoose.model('student', student-schema)
module.exports = student;
After defining schema we defined collection(table) with the help of a mongoose.model method and pass collection name student and schema name student-schema then exports this collection because we need to use in app.js file.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000 ;
const student = require('./model/studentschema')
require('./database/connection')
app.post('/studentregistration', (req,res)=>{
res.send('<h1>this is home page of Student Api </h1>')
})
app.listen(port , ()=>{
console.log(`connection is extablished`)
});
Cool! database connected. The defined schema is working correctly now let's move on to the second part of the blog which is create, read, update, delete (CRUD) operation.
CRUD Operation
Create Data
The POST method sends data to the server. Know more about POST method
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000 ;
const student = require('./model/studentschema')
app.use(express.json())
require('./database/connection')
app.post('/student-registration', (req, res) => {
const user = new student(req.body)
user.save().then(() => {
res.status(201).send(user)
}).catch((e) => {
res.status(500).send(e)
})
})
app.listen(port , ()=>{
console.log(`connection is extablished`)
});
This method will accept name, class, email, phone, address from the req.body
POST method takes two parameters so we passed root and callback function.
The callback function has two parameters req and res. By using req.body we are fetching data from the body and store in our collection(table) by save().
Let's test our post API using postman
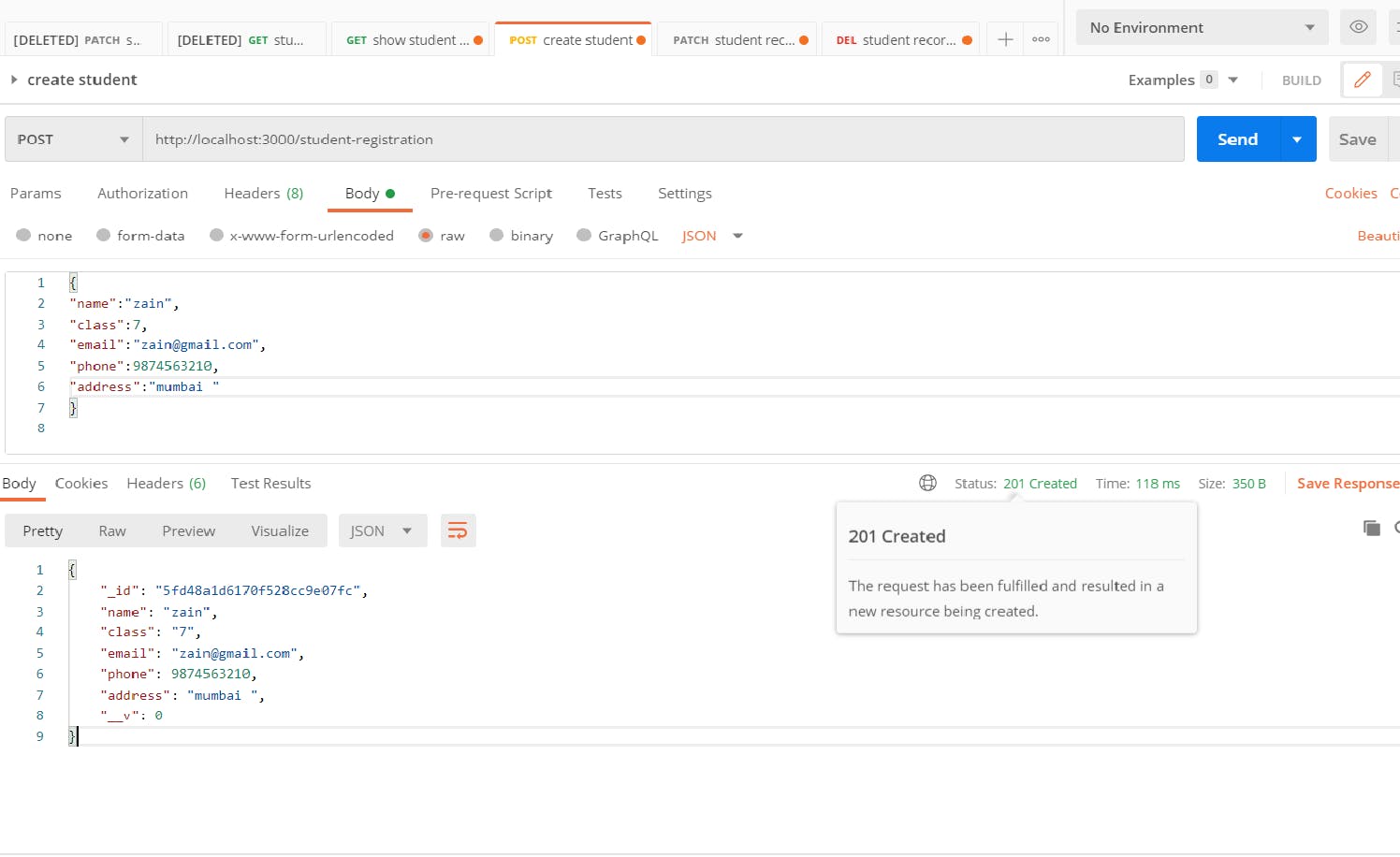
Wow, it's working fine data successful store in our collection.
Read Data
This method will return All Student records. Know more about GET method
Now let’s create a router with our first GET method:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000 ;
const student = require('./model/studentschema')
app.use(express.json())
require('./database/connection')
app.get('/show-student-record', async (req, res) => {
try {
const showStudentData = await student.find()
res.status(200).send(showStudentData)
} catch (e) {
res.status(500).send(e)
}
})
app.listen(port , ()=>{
console.log(`connection is extablished`)
});
.find() return all the student records from student. If the student record cannot be found, the method returns the error message and status code 500.
Let's test our post API using postman
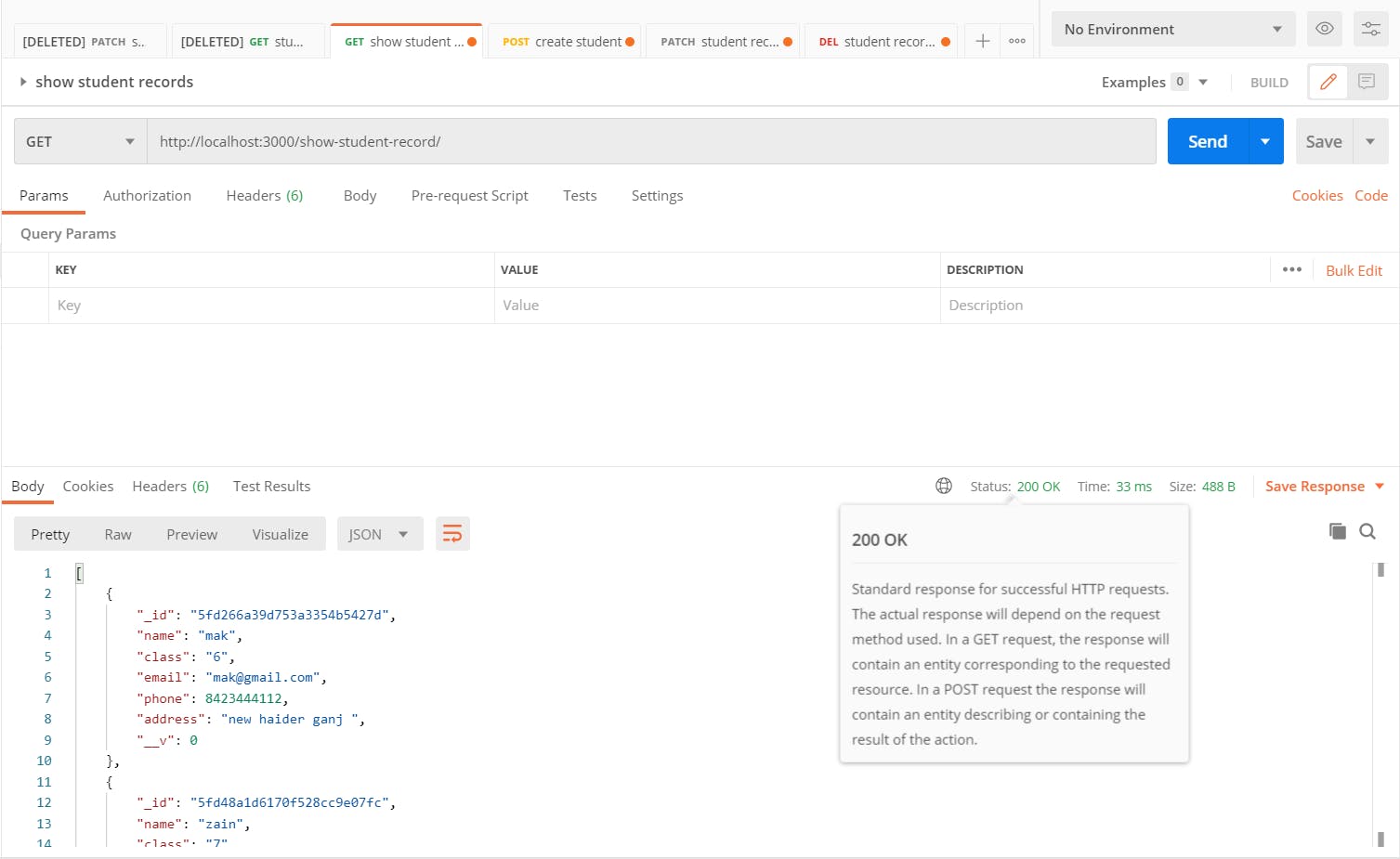
It's working perfectly fine we can see all records in our database
Update Data
PATCH method can be used to update partial resources. For instance, We need to update one field of the resource hence we are using the PATCH method. Know more about PATCH method
app.patch('/student-record-update/:id', async (req, res) => {
try {
const _id = req.params.id;
const studentUpdate = await student.findByIdAndUpdate(_id, req.body, {
new: true
})
res.status(200).send(studentUpdate)
} catch (e) {
res.status(500).send(e)
}
})
Functions need an ObjectID to be able to tell the database which specific document you want to update. ObjectID created automatically when we insert a new record into your database after that we are adding an ObjectID in the URL then we require ObjectID from a URL like this const _id =req.params.id;.
After that findByIdAndUpdate() where the first argument is an _id and a second argument is an Object that will update the data.
Let's test our API using the PostMan
Before updating student record
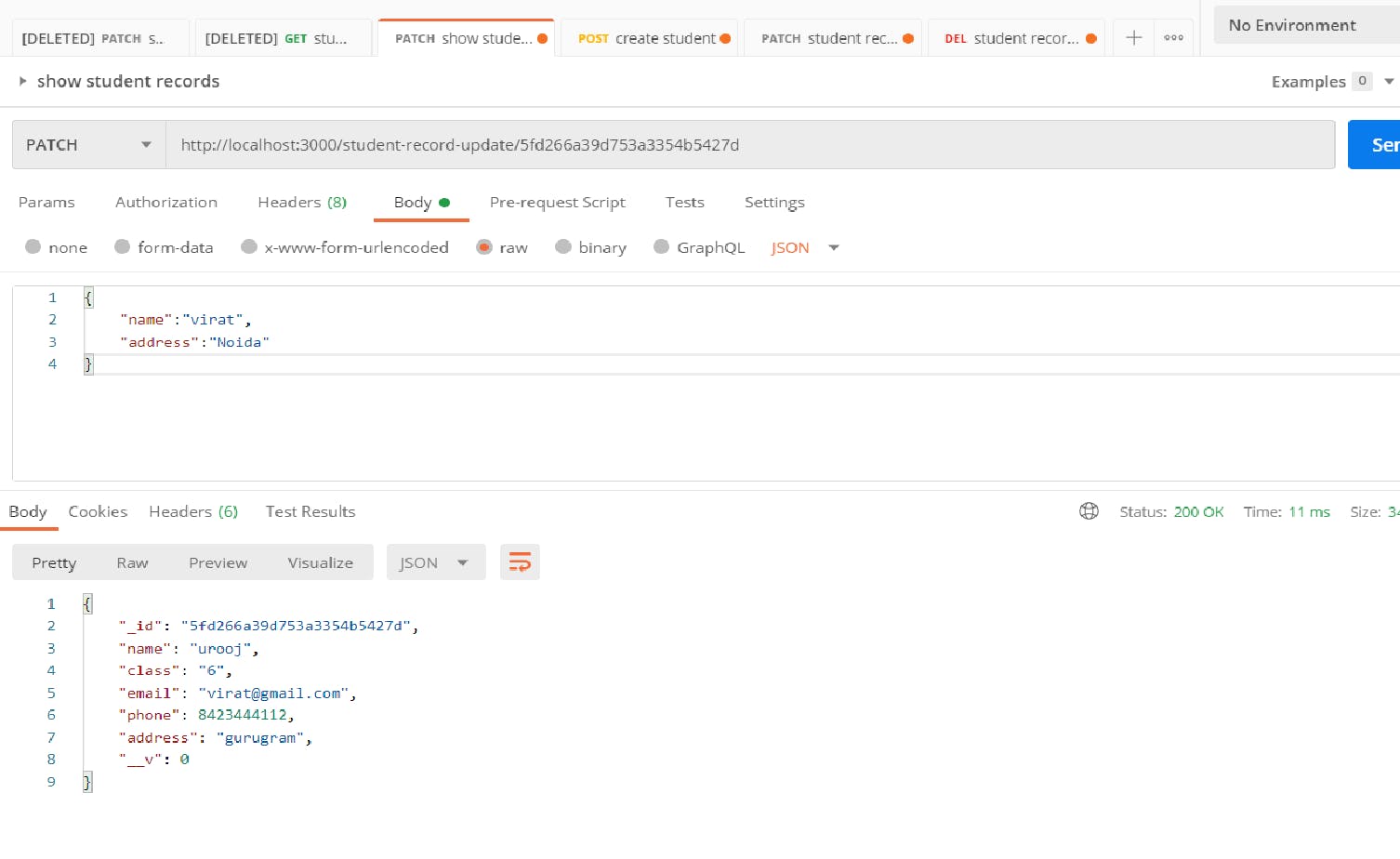
After updating student record
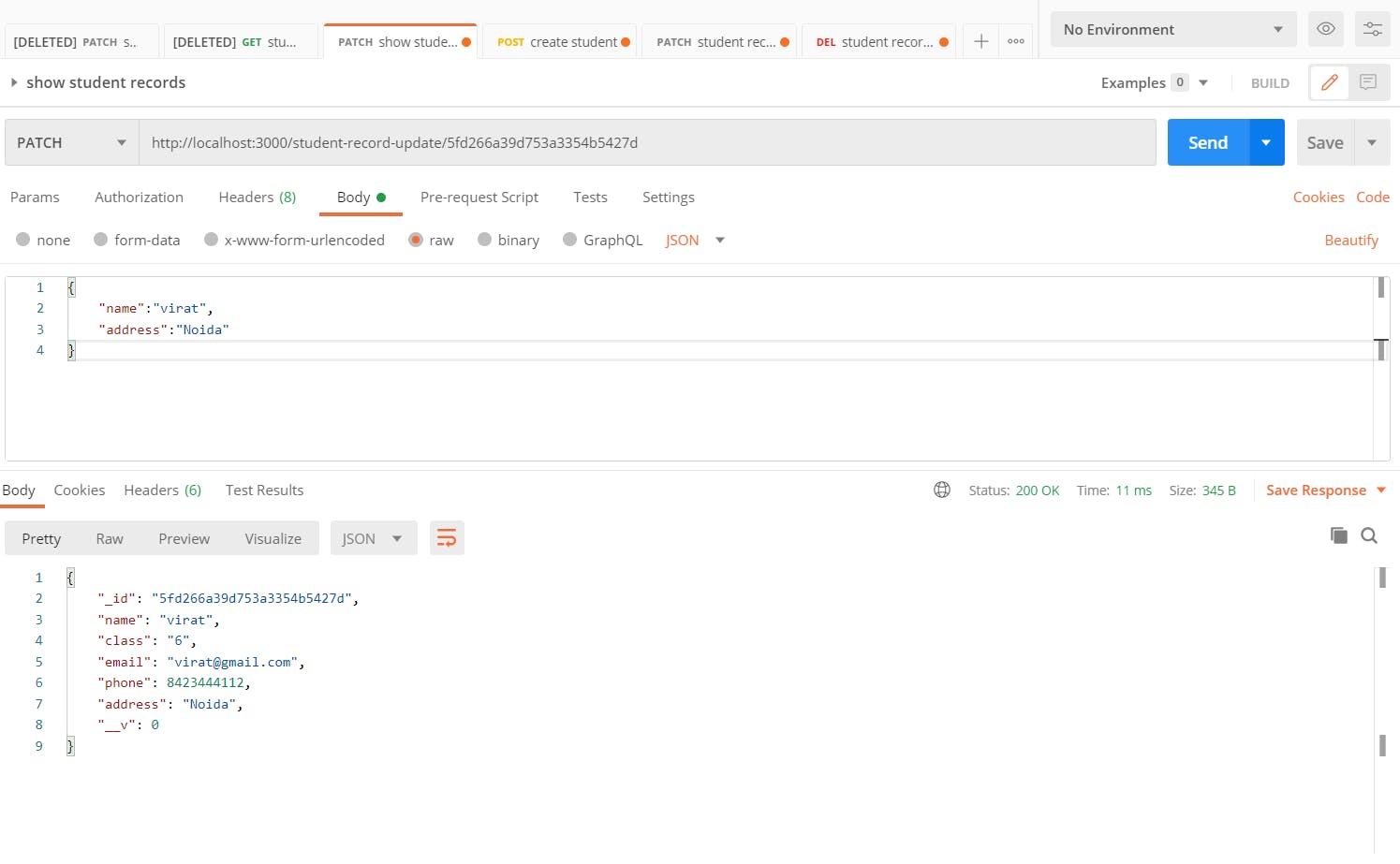
Delete Data
The DELETE method deletes the specified resource. Know more about DELETE method
app.delete('/student-record-delete/:id', async (req, res) => {
try {
const _id = req.params.id
const deleteRecord = await student.findByIdAndDelete(_id)
res.status(200).send(deleteRecord)
} catch (e) {
res.status(500).send(e)
}
})
Functions need an ObjectID to be able to tell the database which specific document you want to delete. It's very similar to a patch request instead of findByIdAndUpdate we are using find findByIdAndDelete where we are passing _id in both arguments like this findByIdAndDelete({_id:_id}) we know that key and value are same so we write like this findByIdAndDelete(_id).
Let's test our API
Before deleting student record
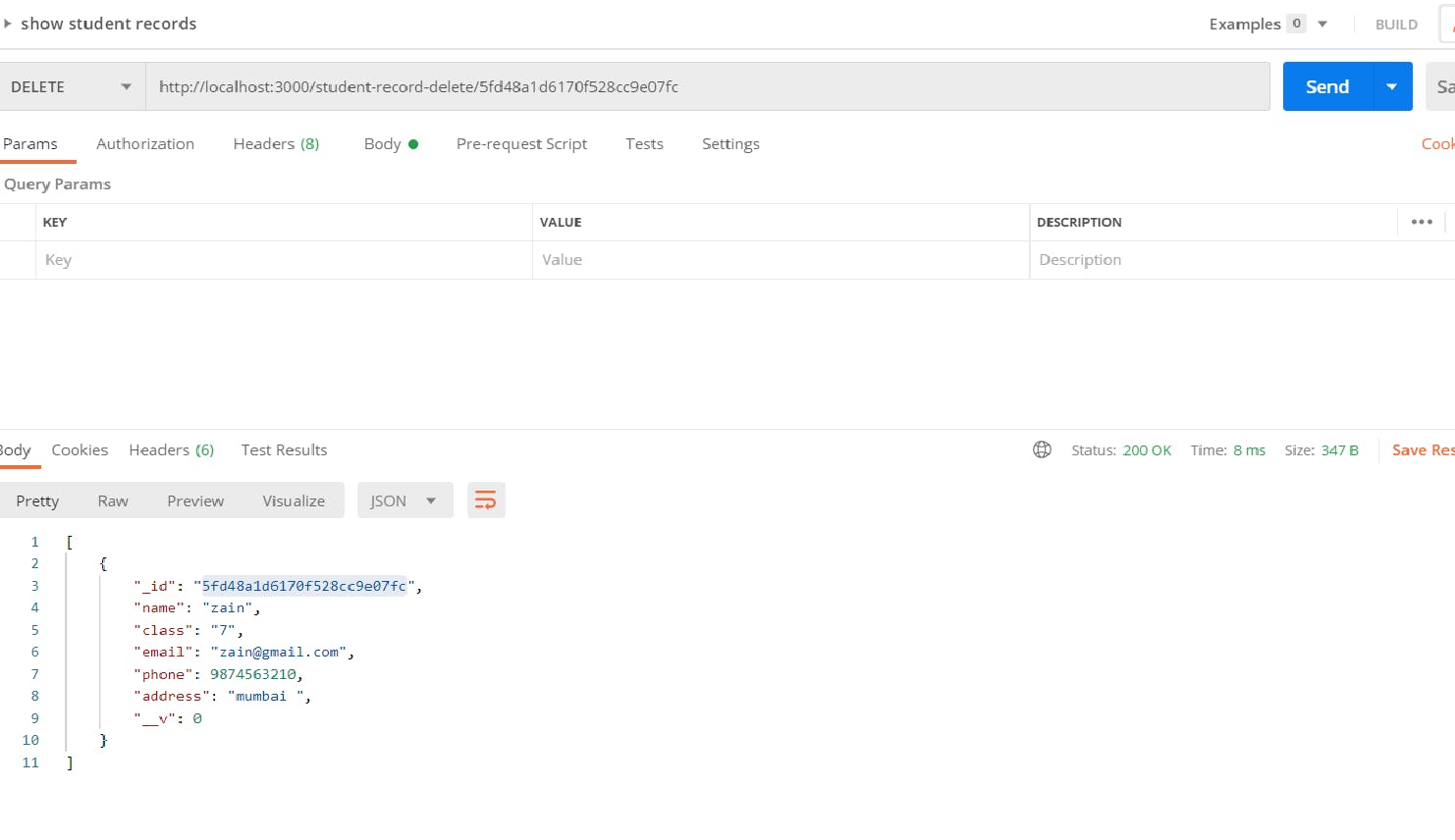
After deleting student record
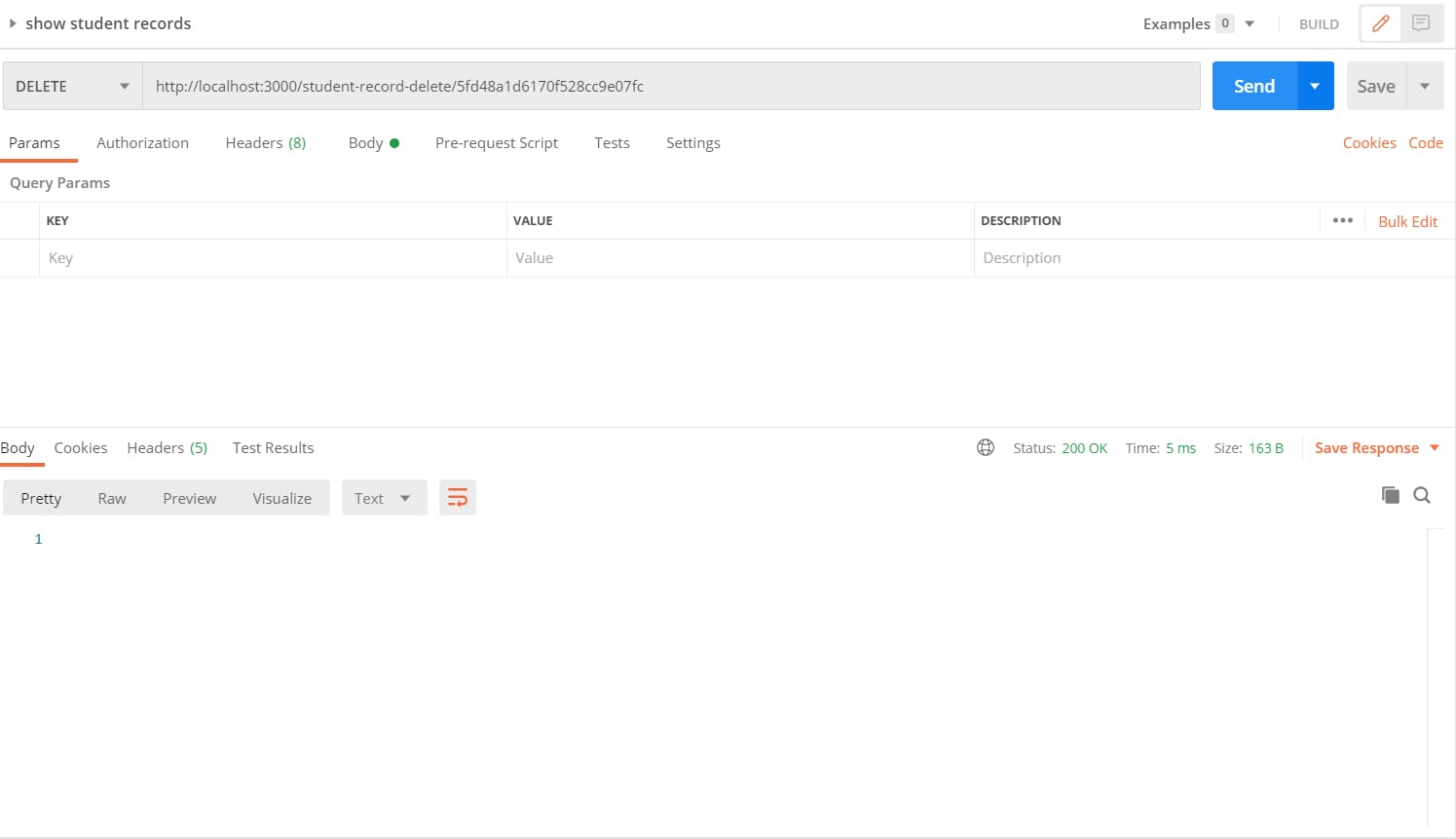
That's it, I hope it was helpful to you. Thanks for reading you can follow me on Twitter
